SCOLIOSIS SHOULD NOT BE OVERLOOKED IT MIGHT HAPPEN TO ALL AGE GROUPS
Scoliosis might be perceived as one of uncommon spinal disorders. In fact, the disease affects 2-3% of Thai population. Scoliosis is defined as a sideways curvature of the spine that occurs most often during the growth spurt just before puberty. However, scoliosis can actually happen in all age groups. The cause of most scoliosis cases is unknown while particular conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy are mainly involved. Due to unspecified causes, being aware of scoliosis signs and regular screening largely contribute to effective and timely treatments. Not only to enhance the mobility but appropriate treatment also improves patient’s quality of life.
Get to know scoliosis
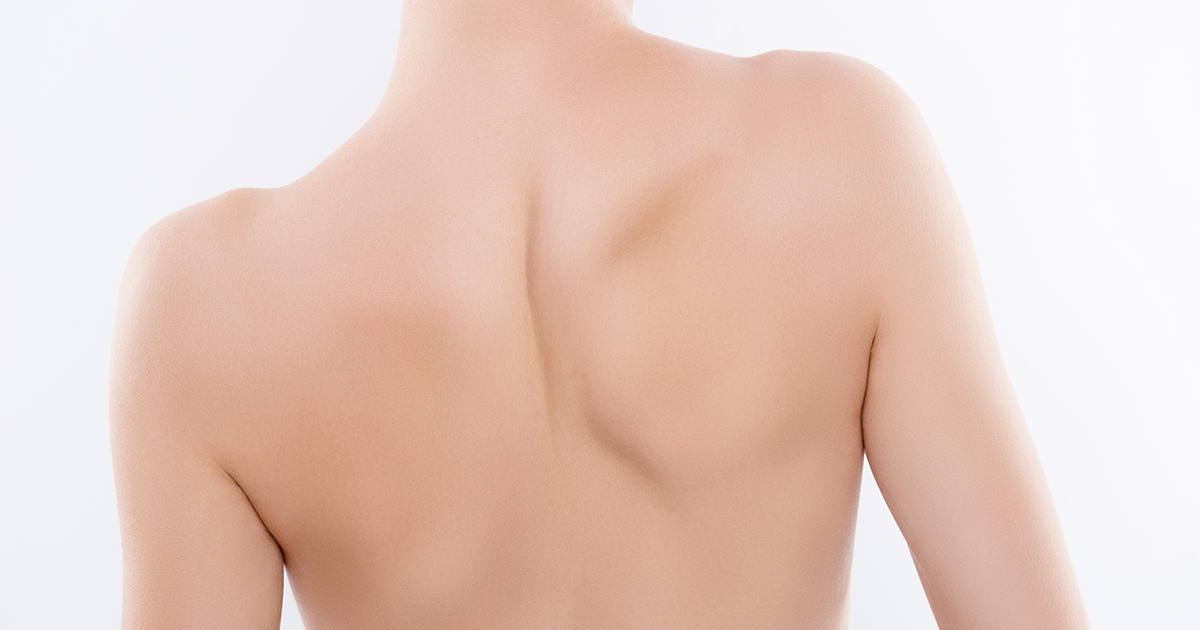
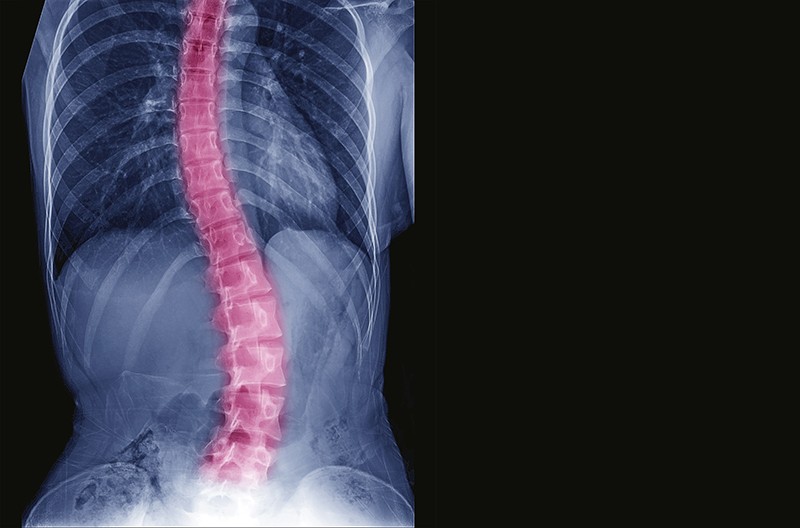
Scoliosis is a spinal deformity in which the spine has a sideways curve. The curve is usually “C” or “S” –shaped. A sideways curvature of the spine subsequently causes uneven shoulders, waist, hips or leg lengths. As a consequence, it considerably impacts body’s movement, range of motion and balance. Eventually, quality of life is largely impaired especially when serious complications arise.
Types of scoliosis
1. Birth defects (congenital scoliosis) resulting from the abnormal development of the vertebral during gestation period. 2. Neuromuscular conditions such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy. 3. Idiopathic scoliosis with no definite cause. The three types of idiopathic scoliosis include:
- Infantile idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosed in children between birth and 3 years of age.
- Juvenile idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosed in children between 4 to 10 years of age.
- Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosed in children between 10 and approximately 18 years of age, accounting for most cases.
4. Functional scoliosis caused by physical abnormalities such as uneven legs, muscular contraction and traumatic injuries. 5. Degenerative lumbar scoliosis which is mostly found in the elderly due to the degenerative changes or overuse. 
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of spinal scoliosis may vary depending on disease severity and individual conditions of each patient. Typical signs and symptoms include:
- Uneven shoulders
- One shoulder blade that appears more prominent than the other
- Noticeable sideways curve
- Asymmetric posture of the body
- Uneven hip
Other related symptoms are back pain, abdominal pain or rib pain and abnormal contraction of muscles. If a scoliosis curve gets worse, the spine might also rotate or twist. This causes serious symptoms affecting the functions of the heart and the lung with the presence of relevant symptoms such as weakness, fatigue , chest pain and breathing difficulties.
Risk factors
Cause of most cases of spinal scoliosis is unknown. Potential risk factors of developing disease involve:
- Age. Spinal scoliosis typically begins during the growth spurt that occurs just prior to puberty period.
- Sex. Girls have much higher risks to develop spinal scoliosis with more disease severity.
- Family history. Scoliosis can run in families. Higher chances to develop this disease are evidenced if there is the presence of family history of scoliosis.
Diagnosis of spinal scoliosis
If warning signs of spinal scoliosis are presented, medical attention must be provided as soon as possible. Diagnostic examinations of spinal scoliosis performed by experienced specialists include:
- A detailed medical history taking e.g. pain characteristics, onset and other health-related issues.
- Physical examination to determine the spinal symmetry during standing and bending forward from the waist, with arms hanging loosely to touch the toes. This test is to identify whether one side of the rib cage is more prominent than the other.
- A balance examination of hips and shoulders.
- A neurological examination to check for muscle weakness, numbness and abnormal reflexes.
- Imaging tests such as X-ray and CT (computerized tomography) scan to visualize spinal abnormalities.
- Advanced imaging test, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan may be additionally used for further investigation.
Complications of spinal scoliosis
While some patients might have a mild form of spinal stenosis, it may sometimes cause serious complications which are:
- Heart and lung damages. In severe cases, the rib cage may press against the lungs and heart, resulting in breathing difficulties and weakness.
- Chronic back pain. Children with scoliosis are more likely to develop chronic back pain than other age groups.
- Self-conscious about appearance. If scoliosis gets worse, it causes more noticeable changes including uneven shoulders, prominent ribs, uneven hips and a shift of the waist and trunk to the side.
Treatment of spinal scoliosis
Based on the guidelines for mild, moderate and severe curves, the decision to begin treatment is always made on an individual basis. Relevant factors to be considered include curve pattern, location of curve, severity of curve and maturity. Treatment options are: Non-surgical treatment In case of moderate scoliosis presented with curves that are between 10-30 degrees, non-operative treatments are physical rehabilitation and proper exercising as well as braces. Wearing a brace is highly recommended in children or teenager with continuous growth of bones and spine. Although it does not cure scoliosis or reverse the curve, it usually prevents further progression of the curve. The brace is normally contoured to conform to the body under the arms, around the rib cage, back and hips. This close-fitting brace is almost invisible under the clothes. Most braces can be worn day and night. With few restrictions, braces do not significantly disturb daily activities. Braces are normally discontinued after the bones stop growing, when there are no further changes in height. This typically occurs approximately two years after girls begin to menstruate or when boys start having hairy organs. During wearing braces, instructions given by specialists must be strictly followed. Surgical treatment Severe scoliosis typically progresses with time. In severe cases that curves are more than 60 degrees with no treatment response obtained from previous non-operative approaches, scoliosis surgery might be recommended in order to reduce the severity of the spinal curve and to prevent it from getting worse. The most common procedure of scoliosis surgery is called spinal fusion. During surgery, two or more of the bones in the spine (vertebrae) are connected together. Pieces of bone or bone-like materials are precisely placed between the vertebrae. Metal rods, wires or screws are typically used to hold the spine straight and still. In some children, if spinal scoliosis progresses rapidly, spine surgeons can surgically place a rod which is adjustable in length as the child grows. This growing rod is attached to the top and bottom sections of the spinal curvature. It is normally lengthened every 6 months in accordance with the growth and curve of bones. Additional spinal surgery to rearrange the position of the vertebrae by using the surgical screws may be required when the child grows up and becomes a suitable candidate. Without delays, children with spinal scoliosis must receive appropriate treatment. Not only to reduce the disease severity, effective and timely treatments also substantially help to slow disease progression, resulting in a better self-confidence and improved quality of life. Reference: Dr. Athikom Methathien Orthopedic and spine surgeon. Spine Center, Bangkok International Hospital.
For more information, please contact Spine Center, Bangkok International Hospital Opening hours: Monday – Sunday 07.00 AM. – 08.00 PM. Tel: 1719 (local call) Email: [email protected]